Lyme Disease
Comprehensive Guide to Lyme Disease
What is Lyme Disease?
Bacterial Origin and Transmission
It is an infection caused by the Borrelia burgdorferi bacterium, transmitted through the bite of infected black-legged or deer ticks. The transmission process is closely linked to the tick’s life cycle and human exposure to tick-infested environments.
Geographical Variance in Prevalence
The occurrence of Lyme disease varies appreciably by region, primarily due to ecological factors favoring deer tick populations.
Transmission and Risk Factors
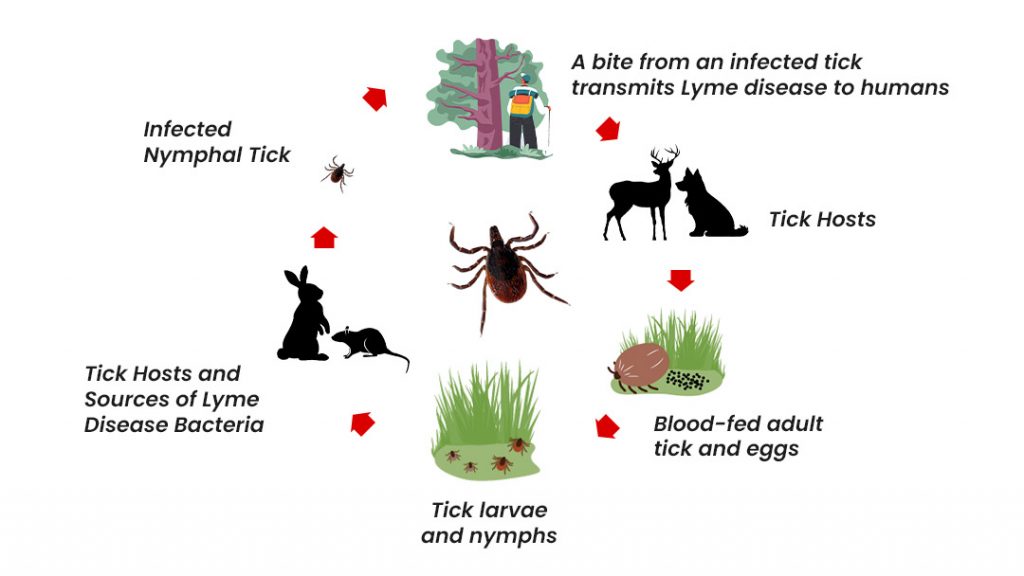
Tick Habitat and Human Exposure
Ticks thrive in wooded, brushy, and grassy areas, including suburban neighborhoods. Understanding tick habitats helps assess the risk of exposure, with those living near or visiting these areas at higher risk, especially during outdoor activities.
Climate Impact on Tick Population
Climate change influences tick populations and their activity periods. Warmer temperatures can extend the tick season and expand their geographical range, potentially increasing Lyme disease transmission.
Animal Hosts and Lyme Disease Transmission
Ticks feed on blood from wild animals like deer and rodents, which are reservoirs for Lyme bacteria. Areas with higher populations of these animals can see increased Lyme disease cases.
Outdoor Activities as a Risk Factor
Engaging in outdoor activities such as hiking, camping, or gardening in tick-infested areas increases Lyme disease risk. The nymphal stage of ticks, which are smaller and more active during warmer months, is particularly responsible for most human Lyme disease cases.
Preventive Measures
Prevention strategies include wearing protective clothing, using tick repellents, performing regular tick checks, keeping pointed tweezers, and managing outdoor spaces to reduce tick habitats.
Symptoms and Stages of Lyme Disease
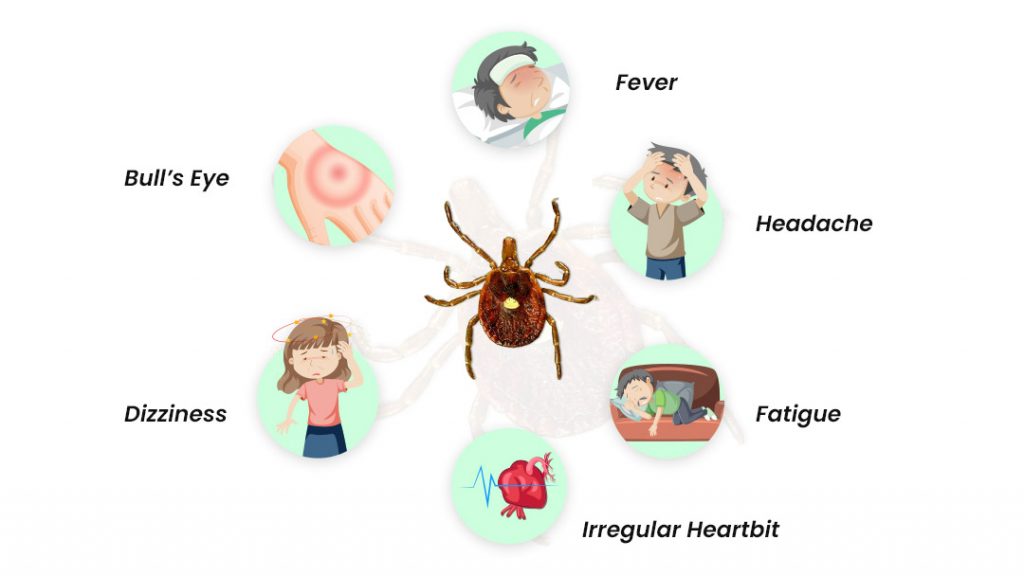
Early Stage Symptoms
Initial symptoms often include the characteristic erythema migrans rash, resembling a bull’s eye, and flu-like symptoms like fever, chills, fatigue, body aches, and headaches.
The Significance of the Erythema Migrans Rash
The erythema migrans rash is a critical early symptom, typically appearing 3-30 days after a tick bite, providing an early indication of Lyme disease.
Symptoms in Later Stages
If untreated, Lyme disease can cause more severe symptoms, including joint pain and swelling, neurological issues like meningitis or facial paralysis, and, in rare cases, cardiac problems.
Late-Stage Lyme Disease Indicators
In the absence of treatment, symptoms can progress to more serious conditions such as Lyme arthritis and neurological manifestations.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Lyme Disease
Diagnostic Approaches
Diagnosis involves recognizing symptoms and may include blood tests, though early testing can sometimes yield false results. A clinical diagnosis is often made based on symptoms and possible tick exposure. Please consult with your doctor / health specialist right away if you suspect tick bite, etc.
Challenges in Lyme Disease Diagnosis
Diagnosing Lyme disease can be complex due to its varied symptoms and the limitations of diagnostic tests, often leading to misdiagnosis.
Treatment Methods
Treatment typically involves antibiotics, with oral antibiotics like doxycycline being effective for most early-stage cases. Severe or late-stage cases may require intravenous antibiotics.
Long-Term Treatment and Post-Lyme Disease Syndrome
Some patients may continue to experience symptoms after treatment, known as Post-Lyme Disease Syndrome (PTLDS), requiring a multidisciplinary approach to management.
Prevention Strategies for Lyme Disease
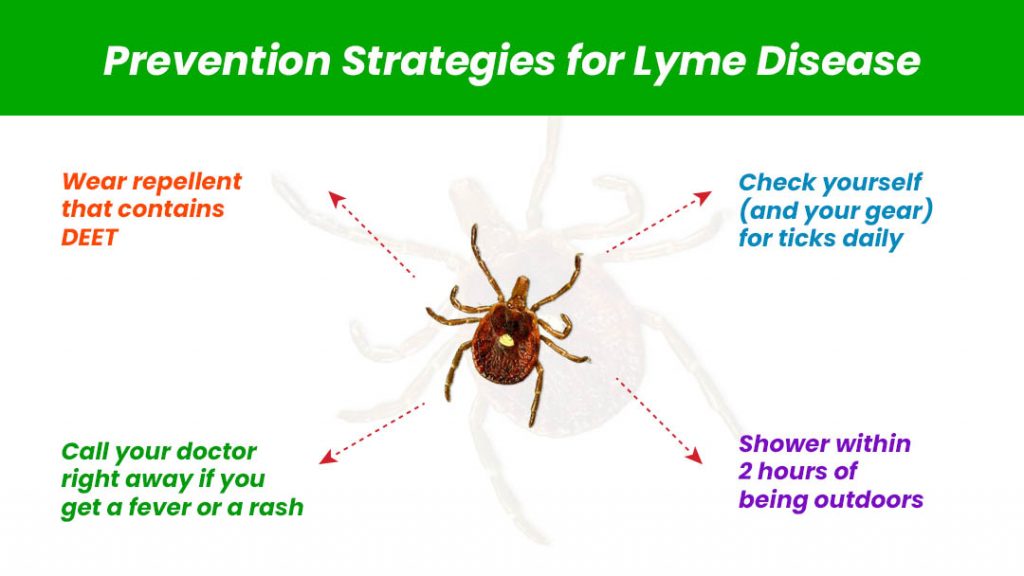
Tick Avoidance and Environmental Management
Effective prevention includes using tick repellents, wearing appropriate clothing, and modifying landscapes to minimize tick populations in residential areas.
Safe Tick Removal Techniques
Proper tick removal, using fine-tipped tick tweezers and avoiding twisting or squeezing the tick, is essential. After removing the tick, thoroughly clean the bite area and your hands with rubbing alcohol, an iodine scrub, or soap and water.
Personal Protective Measures
In addition to repellents and clothing, showering after being outdoors and performing daily tick checks are important preventive measures.
Community and Public Health Strategies
Public health initiatives, such as awareness campaigns and tick surveillance programs, play a crucial role in preventing Lyme disease.
Vaccine Research and Development
Ongoing research into a Lyme disease vaccine could significantly reduce the incidence of the disease in the future.
Living with Lyme Disease
Understanding and effectively managing Lyme disease is essential, particularly in endemic regions. Staying informed about preventive measures, early detection, and treatment options is crucial. Leveraging resources like Hashir Products for effective tick removal and following guidelines from medical professionals can significantly reduce the risks and impacts associated with Lyme disease. Hashir Products offers specialized tick tweezers and tick removal kits that help you remove ticks of all sizes and shapes.
Understanding Lyme Disease
This guide has covered everything from the basics of Lyme disease – how it’s caused by tick bites and varies by region – to detailed aspects like symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment.
Staying Safe and Healthy
We’ve looked at how important it is to be aware of the risks, especially when enjoying outdoor activities. Simple steps like wearing the right clothing, using repellents, and checking for ticks can make a big difference. If you do get bitten, knowing how to safely remove a tick and when to see a doctor can help catch the disease early. It always best to be well informed.
Looking Ahead
The guide also touches on the challenges in diagnosing Lyme disease and why early and accurate treatment is crucial. Living with Lyme disease, especially chronic cases, can be tough, but with the right care and support, it’s manageable. Plus, there’s hope on the horizon with ongoing research into new treatments and potential vaccines.
In short, being informed, taking preventive steps, and seeking timely medical care are key to dealing with Lyme disease. As we learn more and develop better ways to fight it, we can all help keep our communities stay safe and healthy!
FAQs About Lyme Disease

Can Lyme disease recur after treatment?
Yes, it’s possible for Lyme disease symptoms to reappear after treatment, either due to incomplete treatment effectiveness or reinfection from another tick bite. Proper treatment usually prevents recurrence.
Are there specific tests to diagnose Lyme disease?
The ELISA test, followed by the Western blot test, is used to diagnose Lyme disease. These tests detect antibodies to the Lyme bacteria, with increased reliability a few weeks post-infection.
Can Lyme disease be transmitted from person to person?
No, Lyme disease cannot be transmitted from person to person. It is only transmitted through the bite of an infected tick.
Is there a link between Lyme disease and pregnancy complications?
While research is ongoing, untreated Lyme disease might lead to pregnancy complications like infection of the placenta. Proper treatment during pregnancy reduces risks significantly. Please consult with your doctor / health specialist.
Can Lyme disease cause permanent damage?
Untreated Lyme disease can lead to chronic joint inflammation, neurological symptoms, and rare cardiac problems. Early detection and speedy treatment are crucial for preventing long-term complications.
How long does it take to get Lyme disease from a tick bite?
It typically takes 36 to 48 hours of attachment for a tick to transmit Lyme disease to its host. Prompt tick removal is crucial to reduce the risk of infection.
Are there natural remedies for Lyme disease?
While natural remedies may provide symptom relief, they should not replace conventional antibiotic treatments. Always consult with a healthcare professional before trying natural remedies.
What should I do after a tick bite?
After removing the tick, thoroughly clean the bite area and your hands with rubbing alcohol, an iodine scrub, or soap and water. Monitor for symptoms like rash or fever. If symptoms develop, consult a healthcare professional immediately.
Can you get Lyme disease from a deer tick?
Yes, Lyme disease is primarily transmitted via the bite of infected black-legged ticks, commonly known as deer ticks. If you suspect tick bite, consult with your doctor / health professional right away.
What is the best insect repellent for ticks?
Repellents containing DEET, picaridin, or permethrin are effective against ticks. Always follow the instructions on the product label for safe application.
What are the treatment options for Lyme disease?
Lyme disease is typically treated with antibiotics. Treatment options vary depending on the symptoms and stage of the disease.
How can I check for ticks on dogs?
Examine your dog’s coat thoroughly, especially under the collar, behind the ears, between the legs, and around the tail. Feel for any bumps or see if the dog reacts to a tender area.
How can I create a tick-free yard?
Keep lawns mowed, remove leaf litter, trim bushes, and create a barrier with gravel or wood between your yard and wooded areas to reduce tick habitats.
How should I check for ticks after hiking?
After hiking, conduct a full-body tick check, paying close attention to underarms, in and around ears, inside the belly button, behind the knees, around the waist, and in hair.
How do I avoid ticks?
Stick to well-maintained trails and avoid walking through tall grasses or heavily wooded areas. Urban parks and manicured areas are generally less risky for tick exposure.
What should I do if I find a tick on my pet?
Carefully remove the tick with tweezers, pulling it straight up without twisting. Clean the bite area and your hands afterward. Monitor your pet for any signs of illness and consult a vet if concerned right away.
What are the Lyme disease treatment options?
Treatment options for Lyme disease include antibiotics such as doxycycline, amoxicillin, or cefuroxime, prescribed based on the patient’s age, symptoms, and disease stage. Please consult with your doctor / health professioanl.
Are there Lyme disease support groups?
Yes, there are support groups for those affected by Lyme disease. These groups provide emotional support, information, and resources to help manage the condition.
